EMLSR (Enhanced Multi-Link Single Radio)
EMLSR (Enhanced Multi-Link Single Radio) is a key feature introduced in Wi-Fi 7 (IEEE 802.11be). Basically EMLSR is a multi-link operations (MLO) while using a single radio for transmission and reception.
Simple Operation Steps for EMLSR:
Link Setup: Device connects to an AP on multiple links (2.4GHz + 5GHz + 6GHz).
Monitoring: Listens to all links but transmits/receives on one (2.4/5/6GHz) at a time.
Fast Switching: AP schedules when the device switches link (for downlink/uplink).
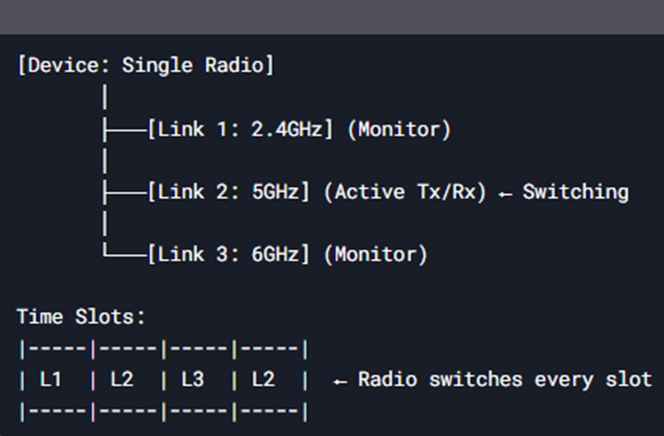
EMLSR Phases:
Association Phase:
Device negotiates supported links (2.4/5/6GHz) with AP.
Monitoring Phase:
Device listens to all links but only decodes Beacons.
Active Phase:
AP schedules Tx/Rx windows via Trigger Frames (IEEE P802.11be D3.0).
EMLSR vs Traditional Wi-Fi:
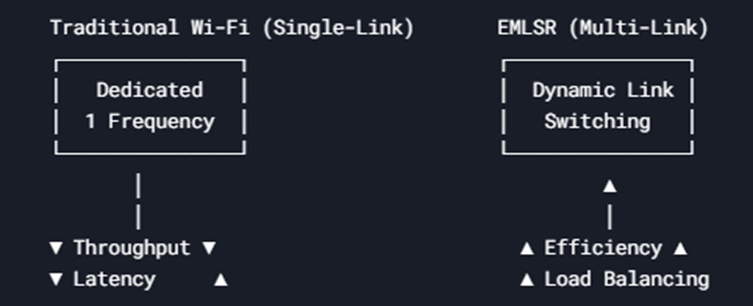
Main comparison between EMLSR and EMLMR:
EMLSR: Uses one radio, switches between links (lower cost, moderate performance).
EMLMR: Uses multiple radios, true simultaneous multi-link (higher performance, more power & cost).
EMLSR Timing Parameters:
| Parameter | Typical Value | Description |
| Radio Switching Delay | 16–32 µs | Time to retune the radio from one band to another. |
| Link Switching Interval | 100–200 µs | Time between switching events (scheduled by AP). |
| Beacon Interval | 100–200 ms | Time between beacon frames (used for synchronization). |
| EMLSR Wakeup Time | ≤ 500 µs | Time for the radio to wake from sleep and switch links. |
| Minimum Switch Duration | ≥ 1 ms | Minimum time spent on a link before switching again. |
Benefits of EMLSR:
- Lower Power Consumption (compared to EMLMR and STR).
- Reduced Hardware Cost (only one radio is enough).
- Better Efficiency than legacy Wi-Fi (avoids idle listening on unused channels).
- Improved Latency & Reliability (faster switching between links than traditional single-link Wi-Fi).
Use Cases:
- Smartphones & Tablets (balance performance and battery life).
- IoT & Wearables (low-power devices with 11be features).
- AR/VR Applications (low-latency requirements without multiple radios).
Real-World Example:
A Wi-Fi 7 smartphone uses EMLSR to:
- Download a file on 5GHz.
- Switch to 6GHz for a video call.
- Monitor 2.4GHz for IoT device signals.
Limitations:
- Not True Simultaneous: Lower throughput than EMLMR.
- Switching Delay: Microseconds lag during transitions.
- Scheduling Complexity: AP must manage link switching precisely.
Conclusion:
EMLSR enables Wi-Fi 7’s multi-link benefits without requiring multiple radios, making it ideal for power-sensitive and cost-constrained devices while still improving performance over Wi-Fi 6.
